Content
- Accumulated Depreciation vs. Accelerated Depreciation
- Is Accumulated Depreciation Considered an Asset?
- Debit and credit journal entry for depreciation expense on PP&E (Property, plant & equipment)
- Where does accumulated depreciation go on the balance sheet?
- Straight-line depreciation expense calculation
- Why Is Accumulated Depreciation a Credit Balance?
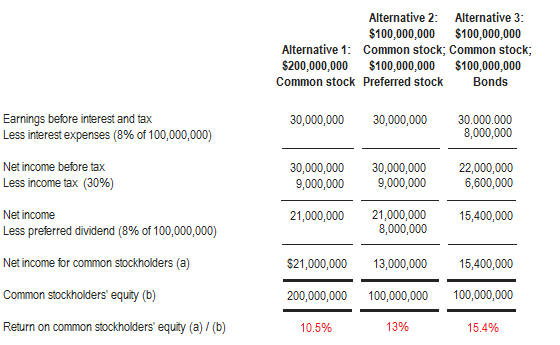
As explained earlier, depreciation expense is a debit and not a credit entry. Let’s look at some examples to show how depreciation expense is a debit and not a credit. In business, every transaction transfers value from credited accounts to debited accounts. Therefore, a credit entry will always add a negative number to the journal whereas a debit entry will add a positive number. A debit will always be positioned on the left side of the account and a credit on the right side of the account. Watch this short video to quickly understand the main concepts covered in this guide, including what accumulated depreciation is and how depreciation expenses are calculated.
So, the company will record depreciation expense of $7,000 annually over the useful life of the equipment. Unlike the other methods, the units of production depreciation method does not depreciate the asset based on time passed, but on the units the asset produced throughout the period. This method is most commonly used for assets in which actual usage, not the passage of time, leads to the depreciation of the asset. While the depreciation expense is the amount recognized each period, the accumulated depreciation is the sum of all depreciation to date since purchase. If a company decides to purchase a fixed asset (PP&E), the total cash expenditure is incurred in once instance in the current period. In accrual accounting, the “accumulated depreciation” on a fixed asset is therefore the sum of all depreciation since the date of original purchase.
Accumulated Depreciation vs. Accelerated Depreciation
This article was co-authored by Darron Kendrick, CPA, MA. Darron Kendrick is an Adjunct Professor of Accounting and Law at the University of North Georgia. He received his Masters degree in tax law from the Thomas Jefferson School of Law in 2012, and his CPA from the Alabama State Board of Public Accountancy in 1984. Depreciation reflects how the value of an asset is used up over time. This article will guide you on what Debits and Credits are, what is Debit and Credit Chart, and how to use them in accounting. The professional preferences of individuals are constantly growing.

The asset is now fully depreciated, and these amounts should stay fixed on the balance sheet until the asset is retired. Which of the following statements is correct with respect to a loss on the sale of a depreciable asset? Explain why depreciation expense, depletion expense, and amortization expense are added to net income in the operating activities section of the statement do you debit or credit accumulated depreciation of cash flows when using the indirect method. The answer is that, in addition to the accounting entries above, we would need to remove the old van from your balance sheet and recognize any gain or loss from the sale of the old van. Let’s assume the net book value remaining for the old van at the time of the trade in was $10,000.00 and you received $8,000.00 for the van.
Is Accumulated Depreciation Considered an Asset?
Explain when to record depreciation expenses when a new asset is purchased. In a journal entry involving only one debit and one credit, is it conceivable to decrease a liability and increase a revenue? In a journal entry involving only one debit and one credit, is it conceivable to increase an asset and decrease a liability?
- Because of this, you need to record the depreciation during each period as an expense on the income statement.
- Accountants use debits and credits to record each business transaction and generate financial statements.
- As a result, accumulated depreciation is a negative balance reported on the balance sheet under the long-term assets section.
- Debits are used to record transactions to accounts that are summarized in the balance sheet and the income statement.
- The purpose of stating accumulated depreciation on the principle balance sheet is to help the readers understand the original cost of an asset and how much of it has been written off.
This helps to ensure that company revenues are matched with the costs of assets used by a company to generate that revenue. Fixed assets, and you’re probably reading this on one right now. Fixed assets are purchases your company makes that add value to the business and that help your company make money.
Debit and credit journal entry for depreciation expense on PP&E (Property, plant & equipment)
In this case, you can head to the financial statement disclosures to find details about the book value of the company’s assets. The depreciation expense recorded flows through to the income statement in the period that it is recorded. Whereas the accumulated depreciation of which the offsetting entry is made is presented on the balance sheet below the line for related capitalized assets.
Why do you credit accumulated depreciation?
Accumulated depreciation has a credit balance, because it aggregates the amount of depreciation expense charged against a fixed asset. This account is paired with the fixed assets line item on the balance sheet, so that the combined total of the two accounts reveals the remaining book value of the fixed assets.
The accumulated depreciation account on a company’s balance sheet is recorded as a contra asset account under the asset section, thus, reducing the total value of assets recognized on the financial statement. The depreciation expense account is debited, each year, expensing a portion of the asset for that year, whereas the accumulated depreciation account is credited for the same amount. As the depreciation expense is charged against the value of the fixed asset over the years, the accumulated depreciation increases. Depreciation is recorded as a debit to a depreciation expense account and a credit to a contra asset account called accumulated depreciation.
How do you record accumulated depreciation?
Depreciation expense is recorded on the income statement as an expense or debit, reducing net income. Accumulated depreciation is not recorded separately on the balance sheet. Instead, it's recorded in a contra asset account as a credit, reducing the value of fixed assets.







